6
INTRODUCTION
OPTICAL ROTARY ENCODERS
What is an encoder
Optical rotary encoders (or shaft encoders) aremade to provide
output signals or digital data based on physical mechanical
measures:
• Rotational speed of the encoder shaft
• Direction of rotation
• Angular position of the shaft
• Linear displacement (with drawwires ormeasuringwheels)
Encoders are used as sensors for motion control, length
measurement and positioning applications
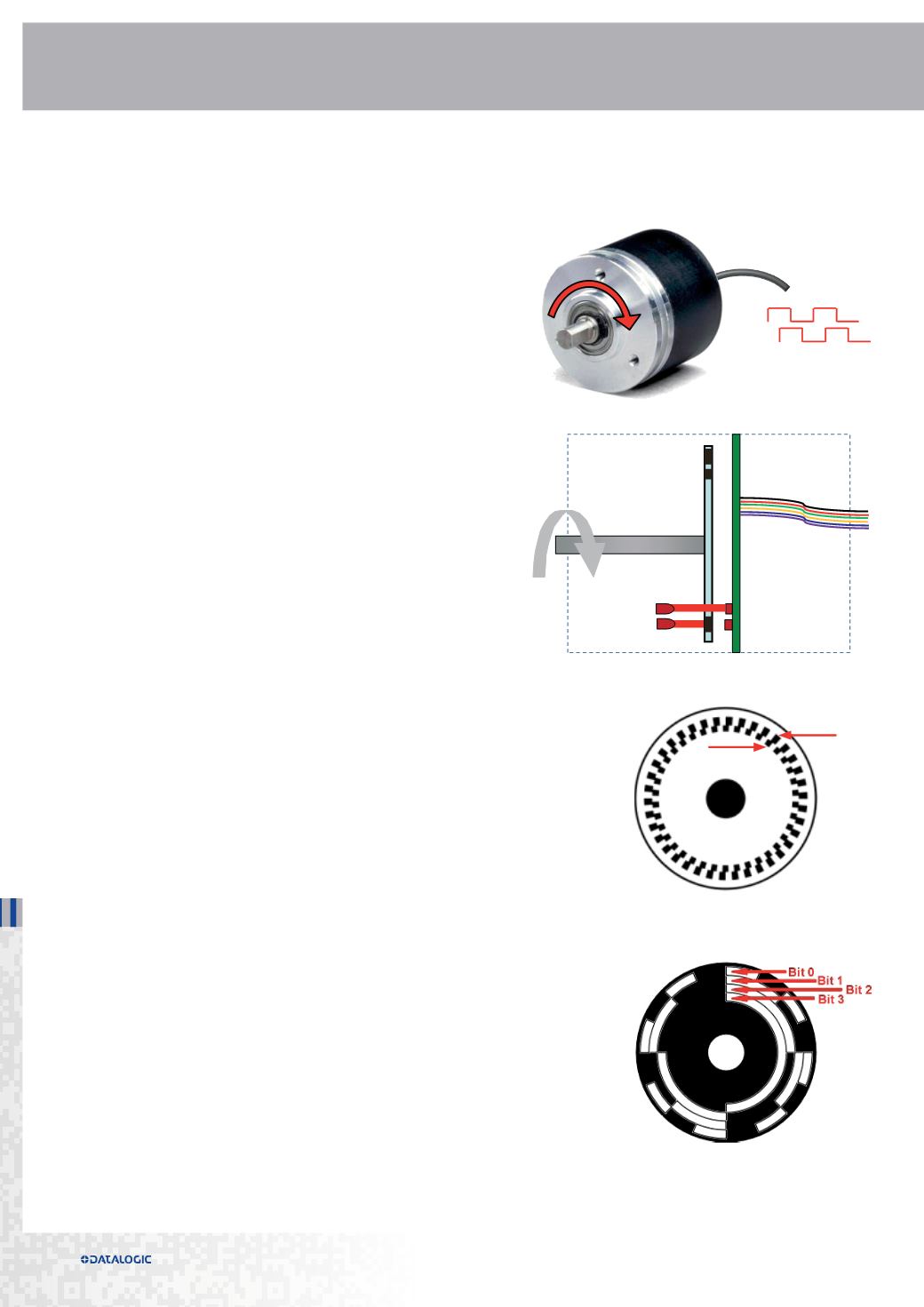
How is made
The encoder shaft transmits the rotation to a coded
disc made of lines which shutter the light from photo-
emitters to photo-receivers, thus generating a variable
electrical signal. According to the different coded disk
mask and electrical circuit there are two types of
encoders: incremental or absolute.
Incremental encoders
Incremental encoders produce sinusoidal or square wave
outputs, which give an incremental number of pulses per
revolution of the shaft.
The resolution is defined as Pulse Per Revolution (PPR).
The signals start at the power up and the shaft position is not retained when
encoder is switched-off, so they can be used to control rotation speed and
direction, but can‘t provide absolute position. A-B-0 (90° phase shifted tracks
and zero) and /A-/B-/0 complement outputs are used to detect rotation
direction, increase resolution and avoid disturbances. The 0 index is used as
reference marker for the “home” position. Datalogic incremental encoders
offer a Smart Push-Pull & Line Driver output which is suitable for both
configurations.
Absolute encoders
Absolute encoders generate a multi-bit digital data information, providing the
actual angular position of the shaft. Single-turn absolute encoders repeat the
code for every shaft revolution. Multi-turn absolute encoders increase the
code at each shaft revolution. Shaft position is retained when the absolute
encoder is switched-off, so it can provide the absolute position, as well as
rotation speed or direction. Absolute encoders have a different bit mask for
each angular position, resolution is defined as Code Per Revolution (CPR) and
also expressed in bits. The simple example shows a 4 bit mask, that’s 16 CPR.
Datalogic absolute encoders are available either with SSI® serial synchronous
interface, or Fieldbus interfaces as CANopen®, Devicenet, EtherCAT, Profibus,
or Profinet.
Track A
Track B
shaft
photo-emitters
photo-receivers
output signals
electrical circuit
coded disk


